Gadolinium Side Effects, Safety Risks and Lawsuits
Gadolinium is a metal that is used in MRI contrast dyes. While it’s effective, some patients report lasting injuries, such as gadolinium deposition disease, nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and toxicity. FDA warnings and lawsuits claim manufacturers failed to disclose these risks.
Our content is developed and backed by respected legal, medical and scientific experts. More than 30 contributors, including product liability attorneys and board-certified physicians, have reviewed our website to ensure it’s medically sound and legally accurate.
legal help when you need it most.
Drugwatch has provided people injured by harmful drugs and devices with reliable answers and experienced legal help since 2009. Brought to you by Wilson & Peterson LLP, we've pursued justice for more than 20,000 families and secured $324 million in settlements and verdicts against negligent manufacturers.
More than 30 contributors, including mass tort attorneys and board-certified doctors, have reviewed our website and added their unique perspectives to ensure you get the most updated and highest quality information.
Drugwatch.com is AACI-certified as a trusted medical content website and is produced by lawyers, a patient advocate and award-winning journalists whose affiliations include the American Bar Association and the American Medical Writers Association.
About Drugwatch.com
- 15+ Years of Advocacy
- $324 Million Recovered for Clients
- 20,000 Families Helped
- A+ BBB Rating
- 4.9 Stars from Google Reviews
Testimonials
I found Drugwatch to be very helpful with finding the right lawyers. We had the opportunity to share our story as well, so that more people can be aware of NEC. We are forever grateful for them.
- Medically reviewed by Jessica Elste, Pharm.D., BCPS
- Last update: December 1, 2025
- Est. Read Time: 8 min read
What Is Gadolinium?
Gadolinium is a rare-earth metal used in contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Since it is toxic in its natural form, gadolinium is bound to larger organic carrier molecules (chelates) through a process called chelation. This makes it safe to use in medical imaging.
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) are created through chelation. They can improve the clarity of MRI scans by altering the way your tissue responds to the magnetic field. This allows radiologists to detect medical problems more easily.
MRI scans with GBCAs help evaluate concerns like inflammatory or infectious diseases in your bones, brain, soft tissue and spine. Globally, GBCAs have been used in over 100 million MRI scans in the past 25 years.
The U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) first approved GBCAs in 1988. Today, multiple brand names of GBCAs exist, including Omniscan (gadodiamide), Magnevist (gadopentetate dimeglumine) and Dotarem (gadoterate meglumine).
Common Side Effects of Gadolinium
Most people tolerate gadolinium contrast without major problems. Some studies estimate that adverse reactions occur in about 0.07% to 2.4% of contrast MRI procedures. Common side effects can include dizziness, headache, nausea or weakness.
- Blood clots
- Cold, warmth or pain at the injection site
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Heart rate changes
- Low blood pressure
- Nausea
- Muscle or joint pain
- Paleness
- Sweating
- Tingling or prickling sensations
- Vomiting
- Weakness
Most gadolinium medicines have similar side effect rates. For example, the most common side effects reported by patients in clinical trials for Gadavist, Magnevist and Omniscan were headache and nausea.
Serious Gadolinium Side Effects
Serious GBCA side effects are rare but can include allergic reactions, gadolinium toxicity and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Some of these complications can be fatal.
If you experience any reactions to gadolinium or have concerns, talk with your doctor immediately.
Allergic Reactions to Gadolinium
In rare cases, you may experience allergic reactions to gadolinium. Your symptoms may manifest as cardiovascular or respiratory issues.
Most reactions occur immediately after administration. Delayed reactions are rare but may occur hours or longer after receiving the medication.
- Blood vessel inflammation
- Cardiac arrest
- Difficulty breathing
- Dizziness
- Eye inflammation
- Fainting
- Hives
- Increased heart rate
- Itching
- Nasal inflammation
- Nausea
- Rash
- Stomach upset
- Swelling in the tissue under your skin
- Vomiting
Severe allergic reactions (hypersensitivity reactions) can be fatal if untreated. Your doctor should discuss your medical history with you before administering gadolinium to determine if you might be at risk of an allergic reaction.
Gadolinium Deposition Disease
Some researchers and medical professionals use the term “gadolinium deposition disease” (GDD) to describe symptoms that occur in patients with normal kidney function after they are exposed to gadolinium.
GDD complications may include:
- Blurry vision or dry eyes
- Bone or joint pain
- Brain fog
- Burning sensations
- Discoloration of your skin
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Insomnia
- Pain
- Pins and needles sensations
- Thickening under your skin
GDD is well-documented, but it is a patient-reported condition. The FDA does not recognize it as an official medical diagnosis.
Gadolinium Retention
Gadolinium retention is similar to gadolinium deposition disease. However, the main difference is that in retention, the gadolinium is slowly excreted from your body over time. With deposition, gadolinium is not eliminated from your body.
The FDA released a safety bulletin in December 2017 warning that gadolinium can remain in certain organs for months or years. GBCAs can linger in the tissues of your bones, brain and kidneys.
Patients who receive numerous GBCAs doses throughout their lifetime have a higher risk of retention.
Gadolinium Toxicity
Gadolinium toxicity hasn’t been studied extensively, and it doesn’t have an established medical definition. However, it generally refers to various rare complications that may occur when your body is exposed to gadolinium through GBCAs.
Anyone can develop gadolinium toxicity, but your risk of developing it may increase if you have kidney problems, receive more than one GBCA injection or have a reactive immune system.
Symptoms of gadolinium toxicity can vary between patients. You may experience:
- Cognitive symptoms
- Dry or bloodshot eyes
- Hair loss
- Itchy skin
- Low body temperature
- Muscle twitching
- Pain or prickling sensations
- Problems with balance
- Swallowing, voice or ear problems
- Swelling in your extremities
- Tight or darkening skin
- Worsening vision
Blood and urine screenings can test for gadolinium toxicity. If you test positive for toxicity, your doctor may prescribe chelation therapy to help remove the gadolinium from your body. This process binds the gadolinium to chelates, allowing it to be excreted from your body.
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis
Gadolinium is linked to nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF). This is a rare but severe condition that causes thickened, darkened skin and possible joint immobility or organ damage.
- Are getting hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis
- Had a kidney transplant, but have compromised renal function
- Have acute kidney injury
- Have moderate or severe kidney disease
These increased risks might be related to your kidneys’ lowered ability to remove GBCAs from your bloodstream.
The first cases of NSF were reported in 2006. These reports prompted the FDA to issue safety warnings advising doctors to screen patients for kidney function before administering GBCAs.
Scientific Evidence Linking Gadolinium To Harm
Manufacturers originally claimed that gadolinium was eliminated from patients’ bodies safely. However, research has proven that gadolinium can harm patients by remaining in the body for extended periods of time, causing dangerous side effects.
Multiple studies, including a 2018 study in Radiology, have confirmed that trace amounts of gadolinium can remain in a patient’s brain, bones and other organs for years after exposure. This risk is seen in patients with normal kidney function and those with compromised function.
Research from 2024 also shows that some patients report persistent symptoms years after MRI exposure, including pain, skin thickening and other potentially life-threatening issues. However, the relationship between retention and these complaints remains debated.
One explanation for retention evaluates the two classes of GBCAs, including linear agents and macrocyclic agents. Studies show that linear agents have weaker gadolinium bonds than macrocyclic agents. This may cause patients who receive linear agents to be at higher risk of gadolinium retention.
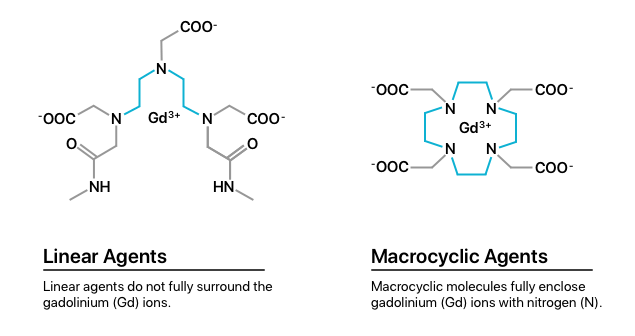
Research found that gadolinium retention from linear agents was 2.9 to 6.5 times higher in bone, brain and skin tissue than from macrocyclic agents.
FDA Warnings and Safety Updates on Gadolinium
As of November 11, 2025, over 91% of gadolinium adverse reactions reported to the FDA’s Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) were classified as serious. The most common side effects reported were NSF, pain and joint stiffness.
| FDA Adverse Event Reports for Gadolinium Side Effects | |
|---|---|
| Total cases reported | 1,635 |
| Serious cases (including deaths) | 1,495 |
| Deaths | 193 |
Over the years, the FDA has issued multiple actions and communications related to gadolinium. These have ranged from approvals to boxed warnings and more.
-
June 28, 1988:
The FDA approved the first gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) for MRI scans.
-
June 8, 2006:
After receiving reports of NSF in kidney patients exposed to gadolinium, the FDA issued its first public health advisory on NSF risk with GBCAs in patients with kidney disease.
-
May 23, 2007:
The FDA required a black box warning on all GBCA labels, cautioning against use in patients with severe kidney impairment.
-
September 9, 2010:
Stronger warnings were added by the FDA, urging clinicians to screen kidney function before administering GBCAs. There were also recommendations to limit use in patients with poor kidney function.
-
December 19, 2017:
The FDA required manufacturers to add new label warnings to all GBCA labels about retention in the body, including the brain, for months to years after receiving GBCAs. This warning included patients with normal kidney function.
-
May 16, 2018:
The FDA approved, issued and required new patient medication guides for GBCAs to better inform patients about gadolinium retention and possible symptoms.
There have been no major recalls for GBCAs in the United States. However, the European Medicines Agency suspended several linear GBCAs in 2017, citing higher risks of long-term retention.
Why People Are Filing Lawsuits Against Gadolinium Makers
Several lawsuits have been filed against manufacturers of GBCAs by patients who experienced NSF, GDD and gadolinium toxicity.
- Failure to warn: Plaintiffs claim that manufacturers failed to adequately warn clinicians and patients about the risks of gadolinium.
- Inadequate testing: Plaintiffs argue that manufacturers failed to conduct sufficient long-term safety studies and ignored early red flags about gadolinium retention.
- Negligence in marketing: Plaintiffs allege that manufacturers marketed these products as “safe” despite evidence of retention risks.
In 2008, plaintiffs successfully formed a federal multidistrict litigation (MDL) to centralize gadolinium cases and expedite the legal process. The MDL was formed in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of Ohio. The case resulted in verdicts worth up to $5 million.
In 2018, plaintiffs attempted to form an MDL against GBCA manufacturer Bayer. The Judicial Panel on Multidistrict Litigation denied the request, ruling that centralization would not improve convenience or efficiency.
While individual lawsuits are still ongoing, gadolinium litigation has remained more limited compared to larger mass torts, including the talcum powder lawsuits.
Patient Stories and Reports
People have spoken out about their experiences with gadolinium, and researchers have published case studies from patients who experienced extreme reactions to GBCAs.
Gena Norris, actor Chuck Norris’s wife, experienced side effects after getting gadolinium for MRI scans. She was in excessive pain and claimed she felt like her whole body was burning. Her doctors didn’t give her a clear answer as to what was causing her symptoms.
Norris also felt mentally foggy and had difficulty moving her arm because of tissue thickening. These symptoms were similar to those of NSF. Even though the FDA says NSF typically affects people with kidney problems, Norris had normal kidney function.
Gena had a difficult time getting better. She stayed at a clinic in Reno, Nevada, for five months while she received IV treatments to remove gadolinium from her body.
A case report from 2020 shared the story of a 45-year-old man who survived anaphylactic shock caused by GBCAs.
After the patient received GBCAs intravenously, he began coughing, experienced shortness of breath, was nauseous and his blood oxygen levels dropped. He then went into cardiac arrest. Lifesaving measures were performed, and he spent 24 hours in the ICU.
He was later discharged and returned home with no deficits after four days.
A 55‐year‐old man was given GBCA and had multiple seizures. Doctors had to intubate him and start him on anti‐epileptic drugs.
Fortunately, he improved after a few days and was discharged from the hospital. He remained on anti-epileptic drugs after discharge.
Alternatives and Safety Considerations
If you need to undergo an MRI using GBCAs, choosing a macrocyclic agent as opposed to a linear one can reduce your risks. Macrocyclic agents create stronger bonds with gadolinium, reducing retention.
If you are a high-risk patient or are worried about the possible side effects of GBRAs, you may opt to get an MRI without the contrast. However, certain situations and diagnoses require contrast for the most accurate results.
Research examining alternatives to reduce gadolinium exposure shows some promising results. An April 2024 study in Nature explored the possibility of using diffusion-weighted imaging for fibroids, finding that it could be a possible alternative to gadolinium.
A separate study published in the Journal of Molecular Imaging and Biology weighed the advantages of using an iron-based contrast agent in lymphatic imaging. The study found that contrast agents based on iron allow for enhanced images without contaminating the patient’s veins.
In addition, advanced imaging methods such as DeepContrast, which uses artificial intelligence and deep learning algorithms, have been proposed to synthesize contrast images with reduced gadolinium doses. While promising, these approaches remain experimental.
The FDA recommends talking with your doctor to discuss your options and weigh the risks against the benefits.
What You Can Do if You Have Side Effects
If you’ve experienced problems after an MRI with gadolinium, the first thing you should do is talk to your doctor. You should also make copies of all your medical records, including treatment dates, doctor visits, test results, side effects you experienced and any diagnosis you receive.
- Talk to your health care provider: Alert your doctor to any side effects you may experience. Do not stop or delay imaging without consulting a health care professional first.
- Request medical records: Keep track of which GBCA you received and when. Also, document any additional diagnoses your doctor makes related to your GCMA exposure.
- Report side effects to MedWatch: Reporting helps regulators monitor emerging risks.
- Consult an attorney: If you were injured by gadolinium, you might be eligible to file a lawsuit. Consider talking to an attorney to understand your options.
If you experienced severe side effects due to gadolinium and want to take legal action, review our gadolinium lawsuit page for the latest information about litigation.
Calling this number connects you with a Drugwatch.com representative. We will direct you to one of our trusted legal partners for a free case review.
Drugwatch.com's trusted legal partners support the organization's mission to keep people safe from dangerous drugs and medical devices. For more information, visit our partners page.