Prevacid
Prevacid (lansoprazole) is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI). Doctors may recommend it for short-term treatment of ulcers and acid reflux. Studies have linked long-term Prevacid use with several serious side effects. Prevacid users have filed lawsuits over complications from the drug.
Prevacid (lansoprazole) belongs to a class of drugs called proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). These are powerful heartburn drugs. Other PPIs include Nexium, Prilosec and Protonix.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Prevacid in 1995. Prevacid is available in prescription and over-the-counter (OTC) versions.
Between 2000 and 2021, several studies linked Prevacid to several serious health risks, especially when taken long-term. Some of the risks associated with Prevacid can result in serious injury or death. These include kidney damage and cancer. Patients have filed Prevacid lawsuits after suffering severe side effects.
People should speak with their doctors before starting or stopping Prevacid.
What Does Prevacid Treat?
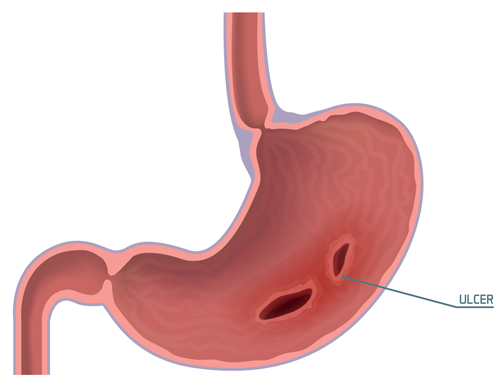
Prevacid treats certain problems related to excess stomach acid. It is generally intended for short-term use — anywhere from 10 days to 12 weeks. But patients sometimes use it for longer periods of time.
FDA-Approved Prevacid Uses
- Treating and maintaining duodenal ulcers
- Certain gastric ulcer treatments
- Treating symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Treatment and maintenance of erosive esophagitis (EE)
- Treating Zollenger-Ellison syndrome and other hypersecretory conditions
- H. pylori treatment
Prevacid is not meant for quick relief of heartburn. It takes up to four days to relieve symptoms.
Lansoprazole is the active ingredient in Prevacid. It is not effective at treating symptomatic GERD in infants.
How Prevacid Works
Prevacid decreases the amount of acid in the stomach. It blocks an enzyme in the stomach wall from releasing acid. Decreased stomach acid gives the stomach and esophagus time to heal. It also prevents further damage and complications. This can prevent ulcers from developing or recurring.
Prevacid vs. Zantac
Prevacid is a PPI, like Nexium and Prilosec. PPIs differ from H2 blockers like Zantac and Pepcid. Both types of medication prevent the stomach from producing too much acid. But they do it in different ways.
Prevacid affects tiny proton pumps that generate acid through a chemical process. Zantac prevents acid-producing cells from responding to histamines in the stomach.
Zantac is advertised to work in as little as 30 minutes. Prevacid can take days and multiple doses to take effect. Zantac was withdrawn from the U.S. market in 2020 and is no longer available. Available H2 blockers include famotidine (Pepcid), and cimetidine (Tagamet).
Serious Prevacid Side Effects, Risks and Warnings
Studies have linked Prevacid and other PPIs to several serious side effects. PPI side effects are most common with long-term use lasting a year or more.
Short-term Prevacid use does not usually cause side effects. When side effects do occur, they are typically mild. Some of the common side effects of Prevacid are constipation, diarrhea, stomach pain and nausea.
Call your doctor right away if you experience any of the following symptoms. They could indicate serious side effects of Prevacid.
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Decreased or bloody urine
- Jerking muscle movements
- Muscle aches or weakness
- Seizures
- Watery or bloody diarrhea
The FDA has issued several Prevacid warnings since 2010.
Prevacid warnings include:
- Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (severe diarrhea that can contain blood or pus)
- Kidney disease and kidney failure due to acute interstitial nephritis (AIN)
- Low magnesium levels
- Lupus erythematosus (autoimmune disease)
- Osteoporosis and fractures of the hip, wrist and spine
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
For a complete list of potential side effects, symptoms and FDA warnings, speak to your pharmacist or doctor and review the drug label.
Prevacid Lawsuits
People who suffered kidney problems have filed Prevacid lawsuits. As of July 2019, there were 12,775 pending lawsuits over several different PPIs.
A federal panel combined the lawsuits in a multidistrict litigation. MDLs allow several similar lawsuits to move more quickly through the legal process. The cases are in New Jersey federal court.
- Acute interstitial nephritis (AIN)
- Kidney disease
- Kidney failure
- Kidney injury
How to Take Prevacid
People take Prevacid orally. It is available in delayed-release capsules and delayed-release orally disintegrating tablets.
Patients can swallow the delayed-release capsules whole. People place the disintegrating tablets on the tongue and allow them to dissolve with or without water.
Patients should take either version before a meal. People should not crush either form of the medicine.
Forms Prevacid Comes In
Prevacid comes in several forms. Over-the-counter and generic prescription versions are available. There are also store brand equivalents. All forms contain the same active ingredient, lansoprazole.
- Prevacid
- Prescription brand-name for lansoprazole; available in capsule form
- Prevacid SoluTab
- Prescription version of Prevacid designed to dissolve; available for suspension in liquids and as a tablet that dissolves in the mouth
- Prevacid 24HR
- Over-the-counter (OTC) version of Prevacid
- Generic lansoprazole
- Generic prescription versions
- Store brands
- Includes Heartburn Relief 24 Hour and Heartburn Treatment 24 Hour; comparable to Prevacid 24HR
Prevacid Dosages
Prescription Prevacid versions come in both 15 mg and 30 mg pills. Prevacid 24 HR comes in 15 mg pills.
Dosages can vary based on the condition Prevacid treats. Doctors may also consider the age and weight of the patient. Doctors may adjust the dosage depending on the patient’s other health conditions.
The recommended daily dosage of Prevacid in people with liver disease is 15 mg.
| Condition Being Treated | Recommended Dose | Taken How Often & How Long |
|---|---|---|
| Duodenal ulcers | 15 mg | Once daily for 8 weeks for short-term treatment Once daily for maintenance of healed ulcer |
| Eradication of H. pylori bacteria – Triple therapy | 30 mg (Prevacid) 1 gram (Amoxicillin) 500 mg (Clarithromycin) | Twice daily for 10 to 14 days |
| Benign gastric ulcer | 30 mg | Once daily for up to 8 weeks for short-term treatment |
| NSAID-associated gastric ulcer | 30 mg or 15 mg | Once daily for 8 weeks for healing Once daily for up to 12 weeks for risk reduction |
| GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) | 15 mg or 30 mg | Once a day for up to 8 weeks for short-term treatment of symptomatic GERD Once a day for up to 8 weeks for short-term treatment of erosive esophagitis (EE) |
| Maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis (EE) | 15 mg | Once a day (controlled studies did not go beyond 12 weeks of treatment) |
| Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome | 60 mg | Once daily (doses and length of time of treatment can vary per patient) |
| Condition Being Treated | Recommended Dose | Taken How Often & How Long |
|---|---|---|
| Short-term treatment of symptomatic GERD and erosive esophagitis (EE) (ages 1 to 11) | 15 mg for kids weighing under 30 kg
30 mg for those weighing more than 30 kg 15 mg for kids weighing under 30 kg 30 mg for those weighing more than 30 kg |
Once a day for up to 12 weeks |
| Short-term treatment of symptomatic GERD (ages 12 to 17) | 15 mg (non-erosive GERD) 30 mg (erosive esophagitis) |
Once daily for up to 8 weeks |
Several recent studies have associated side effects with PPI use in infants. A 2017 study found Prevacid given before a child’s first birthday increased bone fracture risks. And a 2018 study found PPIs taken in infancy can lead to childhood allergies.
Prevacid Overdose and Missed Dose Information
It may be possible to overdose on Prevacid. But a case study found a person who took 20 times the adult dose suffered no adverse reactions.
Tests on rats and mice found no relative overdose risk at 1,300 times the adult dose. Overdose symptoms may include passing out or trouble breathing.
“If over-exposure occurs, call your poison control center at 1-800-222-1222 for current information on the management of poisoning or over-exposure. ”
If a person misses a Prevacid dose, he or she should take a dose as soon as possible. If the person is nearing the time for the next dose, he or she may wait until the next scheduled time.
Prescription vs. Prevacid 24HR (OTC)
Prevacid is available by prescription or over-the-counter (OTC). Prevacid 24HR is the nonprescription version. Studies have found that Prevacid 24HR often works as well as prescription Prevacid. Prevacid 24HR is only available in a 15 mg dose.
People can take one Prevacid 24HR 15 mg pill daily for 14 days. Prevacid 24HR users should not take the drug for more than 14 days. They should wait at least four months before taking Prevacid 24HR again.
Who Should Not Take Prevacid?
People who are allergic to lansoprazole should not take Prevacid. People allergic to any other PPI or other Prevacid ingredient should avoid it.
Ingredients vary with each Prevacid version. Check label ingredients for allergies before taking Prevacid.

People Should Talk with Their Doctor Before Taking Prevacid If They Have:
- Low blood magnesium
- Liver disease
- Lupus
- Allergies to any PPI or PPI ingredient
- Phenylketonuria (PKE)
Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should consult their doctor before taking Prevacid or any other medication.
Prevacid Drug Interactions
Prevacid interactions can happen with 290 other drugs or dietary supplements. People should tell their doctor what drugs they take before starting Prevacid.
Some Prevacid interactions can happen with things as common as aspirin or fish oil.
| Drug | Side Effect |
|---|---|
| HIV Antiretrovirals (including rilpivirine, atazanavir, delavirdine and nelfinavir) | Decreases or increases drug effects |
| Warfarin | Increases risk of bleeding or death |
| Methotrexate | Can lead to methotrexate toxicity |
| Digoxin | Increased exposure |
| Theophylline | Increases clearance of theophylline |
| Drugs dependent on gastric pH for absorption (iron salts) | Reduces absorption |
| Antibiotics (clarithromycin and amoxicillin) | Possible serious adverse reactions, including potentially fatal arrhythmias |
| Tacrolimus | Increases drug’s effects |
| CYP2C19 or CYP3A4 inducers (St. John’s Wort, rifampin and Ritonavir-containing products) | Decreases Prevacid effects |
| CYP2C19 or CYP3A4 inhibitors (voriconazole) | Increases Prevacid effects |
| Sucralfate | Decreases and delays Prevacid absorption |
| Clopidogrel (Plavix) | Decreases effectiveness of Plavix, can increase heart attack risk |
| Aminophylline | May increase aminophylline levels by slowing metabolism, may result in aminophylline toxicity in extremely high doses (interaction is unlikely and effects are minor) |
Calling this number connects you with a Drugwatch.com representative. We will direct you to one of our trusted legal partners for a free case review.
Drugwatch.com's trusted legal partners support the organization's mission to keep people safe from dangerous drugs and medical devices. For more information, visit our partners page.



